The Morning Star Candlestick Pattern is a bullish reversal pattern in technical analysis, signaling the end of a downtrend and the potential start of an uptrend. It represents a shift in market sentiment, where selling pressure weakens, and buying momentum begins to take over.
This pattern is a reliable indicator for traders looking to identify turning points in the market and often serves as a signal to consider long positions. It is typically confirmed with other indicators or increased trading volume for higher accuracy.
What is Morning Star Pattern
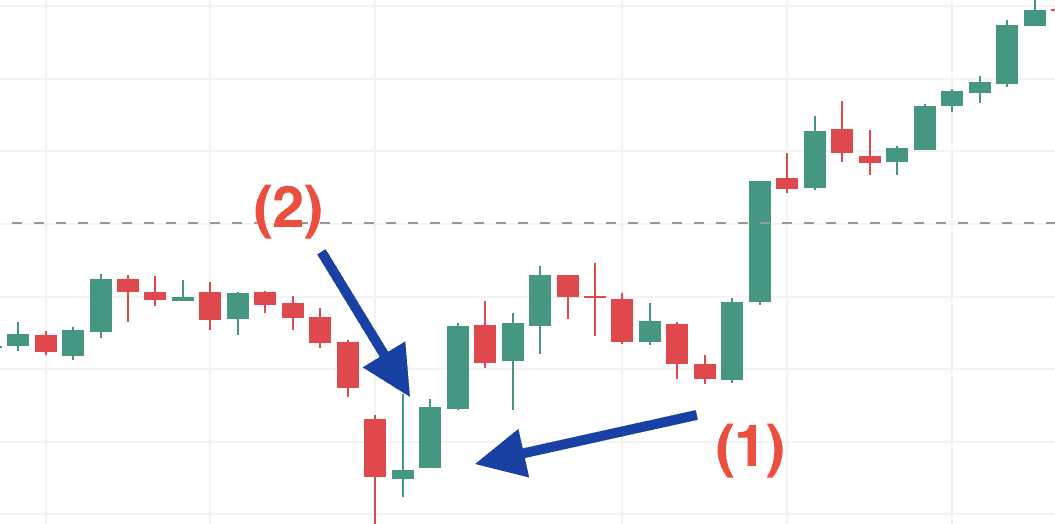
A Morning Star is a pattern in stock charts that signals a possible price reversal from falling to rising. It’s made up of three candles:
- First Candle: A long red (or bearish) candle showing the price is dropping.
- Second Candle: A small candle (red or green) showing the price didn’t change much, indicating hesitation.
- Third Candle: A long green (or bullish) candle showing the price is going up.
This pattern appears after a downtrend and suggests the market might start climbing. To confirm the trend change, traders look for other signs, like higher trading volume or support from other technical indicators.
What Does a Morning Star Tell You?
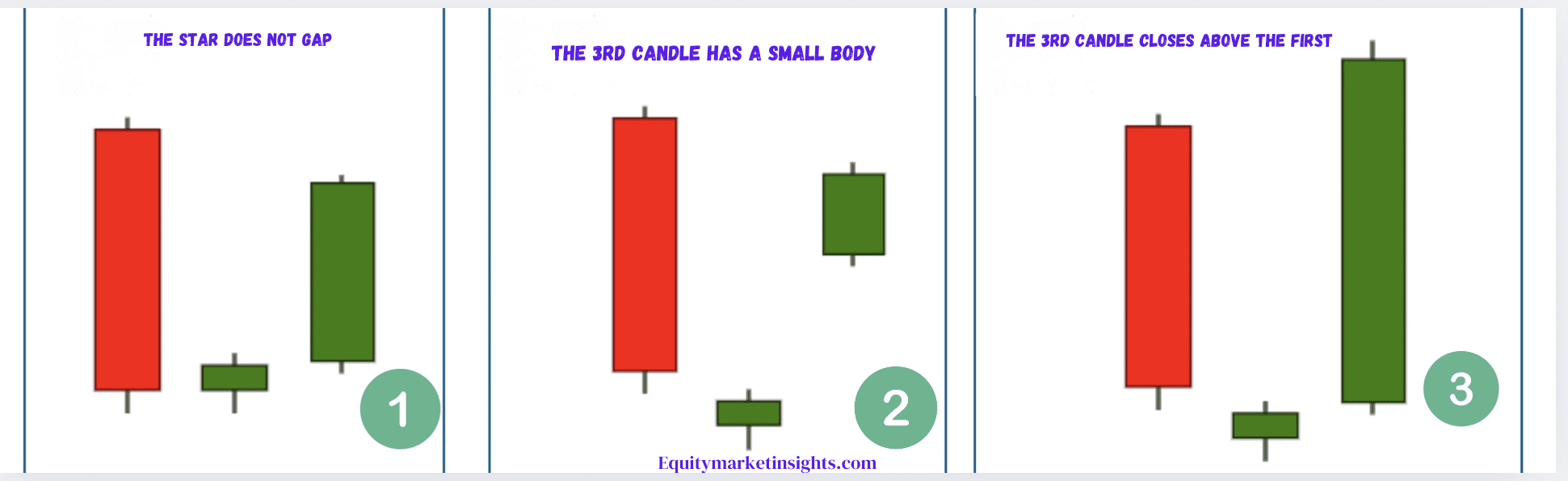
A Morning Star is a visual candlestick pattern, requiring no specific calculations to identify. It consists of three candles, with the lowest point occurring on the second candle. However, this low point is only confirmed after the third candle closes.
To anticipate the formation of a Morning Star, traders may use additional technical indicators. For instance, they might observe whether the price is approaching a support zone or whether the Relative Strength Index (RSI) indicates that the stock or commodity is oversold. These complementary tools enhance the reliability of the pattern as a potential signal for a bullish reversal.
Trading a Morning Star
The Morning Star pattern is a visual indicator of a potential trend reversal from bearish to bullish. Its significance increases when supported by other technical indicators, such as those mentioned earlier. An additional critical factor in validating the pattern is the trading volume associated with its formation.
Ideally, traders look for increasing volume over the three sessions that comprise the pattern, with the highest volume occurring on the third day. This surge in volume on the third session is often regarded as strong confirmation of the Morning Star pattern and the likelihood of an ensuing uptrend, even in the absence of additional indicators.
Traders typically adopt a bullish position in the stock, commodity, pair, or asset as the Morning Star forms during the third session. They then aim to capitalize on the uptrend, monitoring for signals of a potential reversal to exit their position strategically.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the Morning Star Pattern
The Morning Star pattern is a widely recognized candlestick pattern that signals a potential reversal in the market from a downtrend to an uptrend. Traders use this pattern to anticipate changes in market direction and capitalize on the subsequent upward movement. However, like any technical analysis tool, the Morning Star pattern comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Let’s take a closer look at them:
Advantages of the Morning Star Pattern
The Morning Star pattern can be used alongside other technical indicators or chart patterns to confirm the reversal signal. This provides traders with additional confidence and helps to reduce the risk of making trades based on false signals. When the pattern aligns with other indicators, such as momentum or volume, it increases the reliability of the reversal prediction.
User-Friendly: One of the key benefits of the Morning Star pattern is its ease of recognition. Traders, regardless of their experience level, can easily identify this pattern on price charts. The clear three-candle structure—comprising a large bearish candle, a small-bodied candle (which may gap down), and a large bullish candle—makes it accessible and straightforward to interpret.
Versatility: The Morning Star pattern is not limited to a specific market. It can be applied to various financial instruments, such as stocks, forex, commodities, and cryptocurrencies. This versatility allows traders to use the pattern across different asset classes, making it a valuable tool in diverse market conditions.
Reversal Signal: The Morning Star pattern is a reliable signal of potential trend reversals. It marks the shift from a downtrend to an uptrend, providing traders with the opportunity to enter long positions before the market begins its upward movement. This makes it particularly valuable for traders seeking to profit from the early stages of a trend reversal.
Disadvantages of the Morning Star Pattern
Interpretation Plays Key Role: The interpretation of the Morning Star pattern is somewhat subjective. The specific characteristics of each candlestick can vary, and the precise identification of the pattern depends on the perspective and experience of the trader. What one trader sees as a valid Morning Star might be interpreted differently by another, leading to potential inconsistencies in its application.
Can Give False Signals: Like any technical analysis tool, the Morning Star pattern is not foolproof. It can sometimes generate false signals, especially when market conditions are volatile or when the pattern appears during periods of low liquidity. Traders should be cautious and avoid relying solely on the pattern to make trading decisions, as it can fail to predict a reversal in some instances.
Limited Application for Short-Term Trades: The Morning Star pattern is more effective in identifying medium to long-term trend reversals. However, it may have limited applicability for short-term or intraday trading strategies. For traders looking for quick profits in short timeframes, the Morning Star may not be the most suitable pattern. Short-term traders may need to consider additional factors, such as momentum or other intraday indicators, to refine their entry points.
Market Conditions Impact Effectiveness: The reliability of the Morning Star pattern can be influenced by prevailing market conditions, such as overall market volatility and liquidity. In highly volatile or unpredictable markets, the pattern may not perform as expected, leading to reduced effectiveness. Traders must consider the broader market environment before acting on the signal generated by the Morning Star pattern.
How Accurate is the Morning Star Pattern?
Q1. What is the Morning Star candlestick pattern?
A: The Morning Star is a bullish reversal candlestick pattern that signals the potential end of a downtrend and the beginning of an uptrend. It is often used by traders to identify a turning point in market sentiment.
Q2. Why is it called a Morning Star?
A: The pattern is named “Morning Star” because it resembles the appearance of the planet Venus, often called the morning star, which signals the coming of a new day. Similarly, this pattern signals a possible reversal to an upward trend in the market.
Q3. How reliable is the Morning Star pattern?
A: The Morning Star pattern is considered reliable, especially when supported by other technical indicators, such as RSI (Relative Strength Index) or significant trading volume on the third day. However, it should not be used in isolation for trading decisions.
Q4. Does the Morning Star pattern require specific calculations?
A: No, the Morning Star is a visual pattern and does not involve calculations. Traders rely on the formation of candlesticks and additional confirmation from other indicators.
Q5. Where does the Morning Star pattern typically occur?
A: It usually appears at the bottom of a downtrend and indicates a potential reversal to an uptrend. Traders often look for it in support zones or areas of strong buying interest.
Q6. Can the Morning Star pattern appear in any market?
A: Yes, the Morning Star pattern can occur in any financial market, including stocks, commodities, forex, and cryptocurrencies.
Q7. What confirms a Morning Star pattern?
A: Key confirmations for a Morning Star include high trading volume on the third candle, the presence of a support level, and signals from technical indicators such as the RSI or moving averages.
Q8. How do traders use the Morning Star in trading?
A: Traders often enter a bullish position as the third candle of the pattern forms and confirms a reversal. They aim to ride the uptrend and may use stop-loss orders to manage risks.
Q9. Can a Morning Star pattern fail?
A: Yes, like any technical pattern, a Morning Star can fail if the market conditions change or the confirmation signals are weak. Using additional technical analysis and risk management strategies is essential to mitigate this risk.
Q10. What is the difference between a Morning Star and an Evening Star?
A: A Morning Star signals a bullish reversal and appears after a downtrend, while an Evening Star signals a bearish reversal and occurs after an uptrend. Both are three-candlestick patterns but indicate opposite market directions.
